Forecasting future sales is an advantage and a necessity in manufacturing. Without a viable sales forecast, you’ll end up with excess inventory that limits your cash flow and causes disruption on the shop floor. A sales forecasting system allows manufacturers to proactively plan production, minimize waste, and avoid over-committing resources to meet demand.
In this blog, you’ll learn sales forecasting, why it’s important in manufacturing, and how to do it quickly and easily using tools and practical steps.
What is a sales forecast?
A sales forecast is an estimate of future demand for your products based on historical data, industry trends, and current markets. It gives manufacturers the insight they need to effectively plan production schedules, manage inventory, and allocate resources accordingly.
Why sales forecasting is important in manufacturing
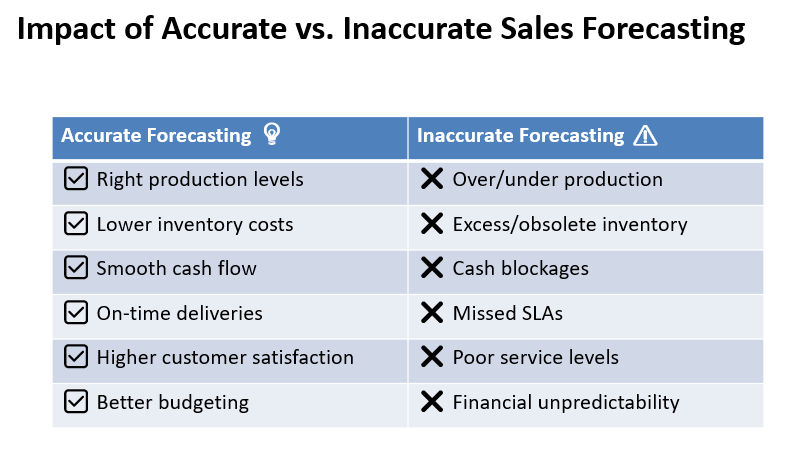
By accurately estimating sales forecasts, manufacturers can:
- Avoid over- or underproduction.
- Reduce carrying costs for excess inventory.
- Improve cash flow and budget accuracy.
- Align purchases with production plans.
- Respond better to market demand.
When forecasts are wrong, the entire supply chain suffers. Excess inventory causes storage costs and possible obsolescence, while shortages and service-level deficiencies lead to late deliveries and dissatisfied customers.
Common challenges in sales forecasting
Manufacturers face the following challenges:
- Inaccurate or unreliable data
- Seasonal or unpredictable demand
- Long lead times
- Variable lead times
- Lack of or low collaboration between teams
- Lack of automation or forecasting tools
Most of these challenges are commonplace. Develop a process and use the right tools to overcome them.
Steps for creating an effective sales forecast
Step 1: Gather the data you need
The first step is to collect high-quality historical sales data, your customers’ ordering behavior, market conditions, and, of course, seasonal demand. Make sure that you also take into account promotional activities or other factors that could affect the accuracy of historical data.
Step 2: Choose the right forecasting method
Different forecasting methods exist. Choose one that is suitable for your product and your customers’ habits in your market.
- Qualitative methods – based on expert knowledge (usually used for a new product)
- Quantitative methods – based on historical sales figures and statistical modeling
- Time series analysis – looks at data over time and finds patterns (usually suitable if you have stable demand)
- Causal methods – utilize external factors such as market conditions, product promotions, etc.
Step 3: Segmentation of products
Products do not follow the same pattern. You need to segment or categorize products, e.g., into high-volume products, seasonal products, low-turnover products, etc. Segmenting products helps with forecasting accuracy and responsiveness to changing conditions.
Step 4: Involve colleagues in other departments
Gather information from departments that represent the business case—sales, marketing, production, finance. Together, these departments provide a more complete picture of future demand than individual forecasts, which could lead to silos.
Step 5: Monitor/adjust/review regularly
A forecast is not a one-time activity. Monitor forecasts monthly or quarterly and compare estimates to actual reported sales each month. Adjust your model based on the business outcomes. Continuous improvement will increase your forecasting success.
Use ERP tools for accurate sales forecasting
Today’s ERP tools, such as ManufApp, enable a faster and more accurate process for estimating future sales. Below are some examples:
- Centralization, cleansing, and integration of sales and inventory information.
- Forecasting algorithms that track trends and influences in real time.
- Accounts for lead times and delivery restrictions.
- Visual dashboards that enable faster decision-making.
- Automatically updates and verifies changes to forecasts.
There are many ways to improve your forecasting processes, especially with the help of an ERP tool. For example, ManufApp can take historical sales data, recognize patterns (good or bad), and extrapolate these into future sales forecasts. This reduces the manual effort in creating forecasts and increases accuracy and transparency.
Conclusion
To summarise, effective sales forecasting is no longer just a “nice to have” but a competitive must-have. By taking practical steps, choosing the right approach, and using smart ERP tools, manufacturers can:
- Align operations with demand
- Reduce costs and waste
- Improve delivery reliability
- Increase customer satisfaction
If you want help setting up accurate forecasting in your manufacturing business, contact the team at ManufApp and get started.