Overview of the Electric Vehicle Industry

Did you know that the automotive industry is currently undergoing a significant transformation, shifting away from fossil fuels and towards electric vehicles (EVs) as part of a sustainable future? With rising concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability, EVs are gaining more appeal. These advanced vehicles don’t just represent an evolution; they signify a revolution in how we drive, power our cars, and reduce our carbon footprint.
While electric vehicles have existed since the late 19th century, it wasn’t until the late 2000s that they began to gain widespread popularity. Nowadays, EVs are gaining traction due to their environmental benefits and cost-efficiency. *In fact, the global EV market was valued at $280 billion as of July 2022, and it is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2026.
But what exactly makes EVs so appealing? For starters, they are incredibly efficient, with electric motors being up to three times more efficient than internal combustion engines. This means that EVs require less energy to travel the same distance as a gasoline-powered car, resulting in lower fuel costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
The shift towards electric vehicles is not only beneficial for the environment but also for the economy and our everyday lives. As more and more people recognize the advantages of EVs, we can look forward to a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Adoption of EVs in India
India is one of the fastest-growing markets for EVs, witnessing the sale of more than 20 Lakh electric cars in just six years since their adoption. The Indian government has introduced favourable policies and subsidies to encourage the expansion of the electric vehicle industry. In 2022, the EV sector saw a 200% growth in sales, with 57,447 automobiles registered in the first month of the year. The two- and four-wheeler segments are being led by Ola Electric and Tata Motors, the two main companies in the Indian electric vehicle market.
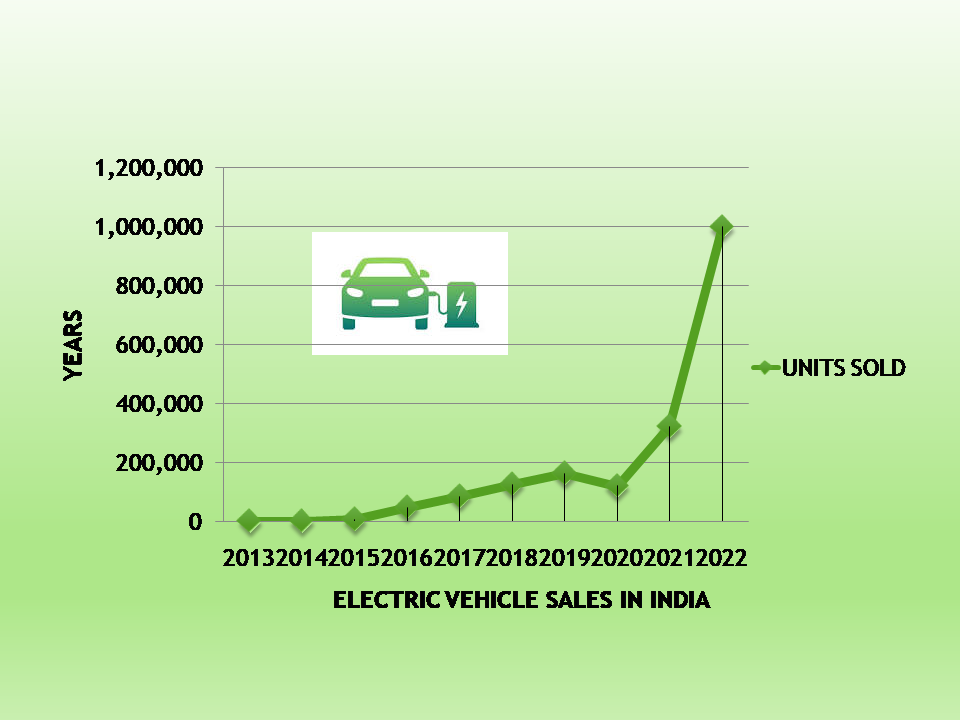
Tata Motors is leading the market in sales with a market share of over 90% in 2023. The electric two-wheeler market is expected to grow by 49% annually between 2023 and 2030, with over 10 million EVs on the road by 2020.
The Indian government has launched several state and central electric vehicle policies to incentivize electric vehicle manufacturers and buyers. These policies include subsidies per kilowatt of electric vehicles for buyers and lower interest rates for manufacturers. The government also provides tax breaks to manufacturers and purchasers on the cost of buying electric vehicles, such as lower tariffs and GST rates.
To boost the rise of electric vehicles in India, the government is collaborating with numerous CPOs to install electric vehicle charging stations across the country. The government is also utilising its purchasing power to encourage EV sales by issuing tenders to procure EVs for government use, such as by putting electric cars and electric buses in their fleet.
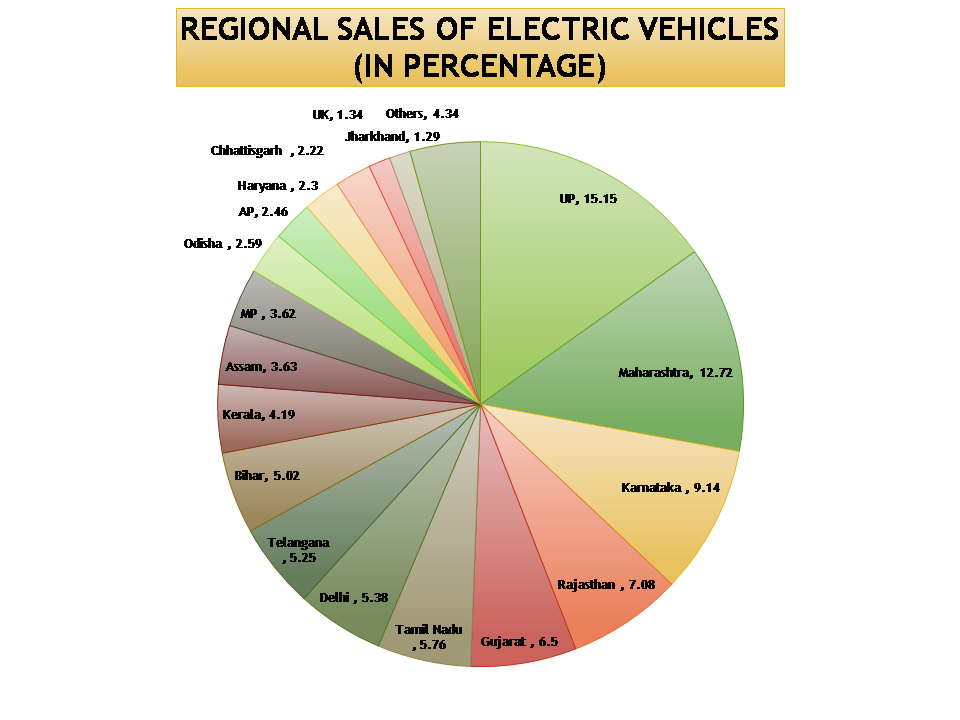
In conclusion, the Indian government’s support and policies are anticipated to continue bolstering the expansion of the electric vehicle market in India. With the rise of EVs, India is well on its way to becoming a leader in sustainable transportation and a pioneer in the EV industry.
How is EV different from traditional manufacturing
| BASIS | TRADITIONAL MANUFACTURING | ELECTRIC VEHICLE MANUFACTURING |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Uses fossil fuels and power from the grid. | Frequently uses renewable energy sources to minimise its impact on the environment. |
| Materials | Traditional vehicles rely on conventional engines and components like gasoline tanks. | EVs often require special materials such as lithium-ion batteries and electric motors. |
| Environmental Impact |
Conventional automobiles release greenhouse gases and harmful pollutants, which play a role in air pollution and contribute to climate change. | EV manufacturing aims to reduce greenhouse gas zero tailpipe emissions, reducing their environmental impact. |
| Maintenance | Traditional vehicles have more moving parts and hence may require more maintenance. | EVs typically have fewer moving parts than traditional vehicles, leading to lower maintenance requirements and costs. They do not require oil changes and have regenerative braking systems that extend brake life. |
| Complexity | Traditional manufacturing focuses on more conventional processes | EV manufacturing is more complex due to the integration of advanced technologies like battery management systems, regenerative braking, and electric drive units. |
| Engine | A combustion engine is used. Here fossil fuels are burned to power cars. To power vehicles, heat energy is turned into mechanical energy. | Rechargeable Electric batteries are employed instead of combustion engines. Electric energy is turned into mechanical energy and used to power vehicles. Generally, renewable sources of energy are used in EVs.. |
Traditional Vehicle Manufacturing Process
Have you ever wondered how automobiles are made? Well, robots play a crucial role in the traditional automobile manufacturing process. They are responsible for designing and shaping the sheet metal components used in constructing the vehicle’s body, which includes side panels, doors, hoods, and roofs. These parts are then combined to create the car’s structure, which is subsequently affixed to the vehicle’s main frame.
As the car moves through the factory, both human workers and robots contribute to the process. The workers stationed along the assembly line join the various parts of the vehicle and occasionally cooperate with robots to complete specific tasks. Autonomous robotic work cells handle tasks such as welding, soldering, screwing, and glueing various components together.
But that’s not all – during the fabrication and attachment of the vehicle’s body parts, additional processes like cleaning, the application of layered chemical coatings to protect against corrosion and scratches, and painting are carried out. Finally, to make the vehicle functional, the engine, transmission, axles, exhaust systems, and tires are all installed.
It’s amazing to see how technology and human expertise come together to create something as complex as an automobile.
EV Manufacturing Process
Electric cars are handcrafted at six workstations using aluminium space frame subassemblies. These prefabricated pieces are welded or glued together, providing a durable and stiffer connection. The undercarriage and upper body sections are bonded, and the body is added to the underbody. The adhesive is cured through a two-stage oven, and the roof is attached. The underbody and frame are coated with protective sealants, and the finished body is moved to the general assembly area.
The production procedure of an electric vehicle is as complex as the vehicle’s design. It requires six workstations to construct the body. Multiple-head torque wrenches are installed at each station, allowing the assembler to choose the appropriate torque setting for the fasteners. The instrument panel and dash are moulded, fibreglass-reinforced urethane, as well as the flooring, seats, and carpets. Since there are fewer pieces required for assembly, performance is greater.
Once the air conditioning, heating, and circulation systems have been inserted and filled, the battery pack is installed. The vehicle is then driven to the last set of workstations, powered up, and inspected before being driven to the following team. Other fluids are added and checked, and the windshield is attached. All connections have been finished and verified, and the door systems have been attached. The upper exterior is finished by the addition of the external panels and the attachment of the last trim.
After the alignment is checked and adjusted at the final workstation, the under-body panel is bolted into place. The operation comes to a close with a complete quality control check that includes pressurised water spraying, a specific test track, and a visual inspection.
We would also light to put a light on our blog on Production Management Software for Electrical Industry which will help you to know the role of PMS on Electrical Industry and benefits of the same.
Sub-Industries involved in EV Manufacturing
Electric vehicle manufacturing involves several sub-industries that contribute to the development, production, and maintenance of electric vehicles. These sub-industries include:
- Battery Manufacturing: One of the critical components of an electric vehicle is the battery pack. Battery manufacturers specialise in producing high-capacity lithium-ion or other advanced batteries used to power electric vehicles.
- Electric Motor Production: Electric vehicles use electric motors for propulsion. Sub-industries involved in motor production create efficient and powerful electric motors that drive EVs.
- Charging Infrastructure: To support electric vehicles, a robust charging infrastructure is essential. Companies involved in this sub-industry design, install, and maintain charging stations.
- Component Manufacturing: Numerous components make up an electric vehicle, including power inverters, DC-DC converters, onboard chargers, and charge ports. Manufacturers specialise in producing these components.
- Automobile Manufacturing: Traditional automobile manufacturers have expanded into electric vehicle production, often with dedicated assembly lines and facilities.
- Research and Development: R&D plays a crucial role in advancing electric vehicle technology. Research institutions and companies invest in developing new materials, technologies, and vehicle designs.
- Government Initiatives: Governments worldwide promote electric vehicle adoption through incentives, regulations, and policies, driving the growth of the electric vehicle industry.
- Suppliers of Raw Materials: Companies that supply materials like lithium, cobalt, and rare earth metals used in battery production are essential to the EV industry.
- Electric Vehicle Ecosystem Development: This includes companies that provide software solutions for EV management, fleet management, and connectivity.
- Recycling and Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainability of electric vehicles involves recycling batteries and reducing environmental impact, creating a sub-industry focused on sustainability practices.
*https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_vehicle
